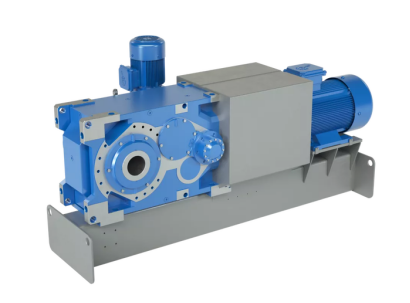
Hoist gearboxes play a crucial role in converting high-speed, low-torque motor power into low-speed, high-torque output, enabling the lifting of heavy loads. This article delves into the intricacies of hoist gearboxes, covering their working principles, selection criteria, and maintenance tips. By understanding these aspects, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your hoisting equipment.

How Does a Hoist Gearbox Work?
A hoist gearbox typically consists of a series of gears arranged in a specific configuration to achieve the desired speed reduction and torque amplification. The basic principle of operation relies on the concept of gear ratios.
1. Gear Ratio:
- Gear Ratio: The ratio of the number of teeth on two meshing gears determines the speed reduction and torque amplification. A higher gear ratio results in a lower output speed and a higher output torque.
- Gear Arrangement: Gearboxes can employ various gear arrangements, including spur gears, helical gears, bevel gears, and worm gears, to achieve specific speed reduction and torque requirements.
2. Power Transmission:
- Motor Input: The electric motor, which provides the initial power input, is connected to the input shaft of the gearbox.
- Gear Meshing: The motor’s rotational motion is transmitted through the gearbox’s gear train. As the gears mesh, they transfer power from one gear to the next, gradually reducing the speed and increasing the torque.
- Output Shaft: The final gear in the train is connected to the output shaft, which drives the hoisting mechanism, such as a drum or pulley system.
3. Torque Amplification:
- Torque Multiplication: The gearbox effectively multiplies the input torque, allowing the hoist to lift heavy loads that would otherwise be impossible with the motor’s direct output.
- Mechanical Advantage: The gear ratio determines the mechanical advantage of the gearbox, which is the ratio of the output force to the input force.
Key Components of a Hoist Gearbox
- Gears: The core components of the gearbox, responsible for transmitting power and altering speed and torque.
- Shafts: Transmit power between the gears.
- Bearings: Reduce friction and support the rotating components.
- Housing: Encloses the gearbox components and provides protection.
- Lubrication System: Ensures smooth operation and reduces wear.

How to Select the Right Hoist Gearbox?
Choosing the right hoist gearbox is crucial for ensuring the efficient and safe operation of your lifting equipment. Here are the key factors to consider when making your selection:
| Load Capacity | Maximum Load: Determine the heaviest load the hoist will need to lift. The gearbox must be capable of handling this load without overloading. |
| Safety Factor: Consider a safety factor to account for unexpected loads or variations in operating conditions. | |
| Lifting Speed | Required Speed: Determine the desired lifting speed for your application. A faster speed may be necessary for high-productivity tasks, while a slower speed might be suitable for precise positioning. |
| Gear Ratio: The gearbox’s gear ratio directly influences the lifting speed. A higher gear ratio results in a lower speed and higher torque, while a lower gear ratio yields a higher speed and lower torque. | |
| Duty Cycle | Operating Conditions: Assess the frequency and duration of the hoist’s operation. Heavy-duty applications require gearboxes designed for continuous or frequent use, while intermittent use applications can tolerate less robust gearboxes. |
| Thermal Considerations: High-duty cycle applications may generate significant heat, so the gearbox must be adequately cooled to prevent overheating and premature failure. | |
| Power Source | Motor Power: Select a gearbox compatible with the power rating of the driving motor. The motor must be able to deliver sufficient power to drive the load at the required speed. |
| Efficiency: A high-efficiency gearbox minimizes energy consumption and reduces operating costs. | |
| Mounting Configuration | Space Constraints: Consider the available space for mounting the gearbox. Different gearbox configurations, such as foot-mounted, flange-mounted, or shaft-mounted, can accommodate various installation requirements. |
| Orientation: Ensure the gearbox can be oriented correctly to align with the motor and the driven component. | |
| Environmental Conditions | Temperature Range: The gearbox must be capable of operating within the expected temperature range. Extreme temperatures can affect lubrication and material properties. |
| Humidity and Corrosion: If the gearbox will be exposed to moisture or corrosive environments, select a model with appropriate protection, such as sealed housings or corrosion-resistant materials. | |
| Noise Level | Workplace Noise: Consider the noise level generated by the gearbox, especially in enclosed environments. Low-noise gearboxes can improve workplace comfort and productivity. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Lubrication: Assess the frequency and type of lubrication required. Some gearboxes have sealed bearings that require minimal maintenance, while others may need regular lubrication. |
| Accessibility: Ensure easy access to lubrication points and other maintenance components. | |
| Cost | Budget: Consider the initial purchase cost and ongoing maintenance costs. While it’s tempting to choose the cheapest option, a higher-quality gearbox may offer better performance, reliability, and longevity, saving money in the long run. |

How to Maintain a Hoist Gearbox?
Proper maintenance of a hoist gearbox is essential to ensure its longevity, efficiency, and safety. Here’s a detailed guide to help you keep your gearbox in top condition:
Regular Inspections
- Visual Inspection: Regularly check the gearbox for any signs of damage, leaks, or excessive wear. Look for cracks, dents, or corrosion on the housing.
- Oil Level: Ensure the oil level is within the specified range. Low oil levels can lead to overheating and premature wear.
- Oil Condition: Check the oil’s color and consistency. Dark, cloudy, or metallic oil indicates contamination or degradation and needs to be replaced.
- Gear Teeth: Inspect the gear teeth for wear, chipping, or pitting. Excessive wear can reduce efficiency and increase noise levels.
- Bearings: Listen for any unusual noises from the bearings, which may indicate wear or damage.
- Seals: Check the seals for leaks. Replace any damaged seals promptly.
- Belts and Chains: If applicable, inspect belts and chains for wear, tension, and alignment.
Lubrication
- Lubricant Type: Use the lubricant recommended by the manufacturer.
- Lubrication Schedule: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended lubrication schedule.
- Lubrication Method: Use the appropriate lubrication method, such as oiling, greasing, or mist lubrication.
- Cleaning: Before lubricating, clean the components to remove dirt and debris.
Temperature Monitoring
- Temperature Sensors: Install temperature sensors to monitor the gearbox’s operating temperature.
- Overheating Prevention: Take steps to prevent overheating, such as ensuring adequate ventilation and proper lubrication.
Load Testing
- Periodic Load Tests: Conduct periodic load tests to verify the gearbox’s capacity and performance.
- Safety Factor: Ensure the load tests are conducted within the gearbox’s rated capacity and safety factor.
Environmental Factors
- Moisture and Corrosion: Protect the gearbox from moisture and corrosive environments.
- Dust and Debris: Keep the gearbox clean and free from dust and debris.
Professional Maintenance
- Regular Servicing: Schedule regular professional maintenance to ensure the gearbox is in optimal condition.
- Expert Inspection: Qualified technicians can identify and address potential issues.
Key Takeaways
Hoist gearboxes are indispensable components in numerous industries. By understanding their working principles, selecting the right gearbox for specific applications, and implementing proper maintenance practices, you can significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of your lifting operations. Remember that regular inspections, timely lubrication, and professional maintenance are key to prolonging the life of your hoist gearbox and preventing costly breakdowns. If you still have any questions about the hoist gearboxes please contact the hoist gearbox supplier CPTC for the information.
Related Products
Suspended Platform Safety Lock
Easy to Operate and Use
Made…
Rope Presser
Wire rope protection
Strengthens wire rope
Improves safety…
Bronze & Brass Worm Wheel
Precise control for smooth operation
Simple…
Construction Platform
With a lightweight…