Safety ropes as one of the most important construction safety devices, provide a lifeline for workers at height, reducing the risk of serious injury or fatality. However, to ensure their effectiveness, safety ropes must be properly inspected, selected, stored, and used. This guide will delve into the essential aspects of safety rope maintenance, selection, storage, and training, empowering you to maximize their performance and minimize risk.

How Often Should Safety Ropes Be Inspected?
Inspection Frequency
Safety ropes should undergo a meticulous inspection before every use, without fail. Additionally, regular inspections should be conducted as outlined in the manufacturer’s specific guidelines. These guidelines often stipulate inspection intervals, which may vary depending on factors like usage frequency, environmental conditions, and the type of rope.
Key Inspection Points
During inspections, look for the following signs of wear and tear:
- Fraying: This occurs when fibers at the rope’s end or along its length begin to separate.
- Cuts: Any nicks or cuts in the rope’s outer sheath can compromise its structural integrity.
- Discoloration: Significant color changes, especially in critical areas, may indicate internal damage.
- Stiffness or Rigidity: A loss of flexibility can be a sign of aging or damage.
- Chemical Damage: Exposure to harsh chemicals can degrade the rope’s strength.
Retirement Criteria
If any of these issues are identified during an inspection, the rope should be immediately retired from service and replaced. Compromised safety ropes pose a serious risk to workers and must not be used under any circumstances.

What Factors Should I Consider When Choosing a Safety Rope?
When choosing a safety rope for construction or other hazardous work environments, it’s crucial to prioritize several key factors:
| Tensile Strength | Weight Capacity | The rope must be robust enough to support the weight of the worker, along with any necessary tools or equipment. |
| Dynamic Load | Consider the potential impact forces that the rope may encounter during a fall arrest event. A higher tensile strength will better absorb these forces. | |
| Flexibility | Maneuverability | A flexible rope is easier to handle and navigate in various work scenarios, reducing the risk of accidental snags or tangles. |
| Comfort | A supple rope can enhance comfort during extended use, especially when working in confined spaces or awkward positions. | |
| Durability | Abrasion Resistance | The rope should be resistant to wear and tear from contact with rough surfaces or sharp edges. |
| UV Resistance | Exposure to sunlight can degrade the rope’s strength over time. Opt for UV-resistant materials to prolong its lifespan. | |
| Chemical Resistance | If the work environment involves exposure to chemicals, choose a rope that is resistant to their corrosive effects. | |
| Certification and Standards | EN 1891 | Ensure that the rope adheres to the European standard EN 1891, which specifies performance requirements for personal protective equipment against falls from height. |
| Manufacturer’s Guidelines | Follow the manufacturer’s specific recommendations for usage, inspection, and maintenance. | |
| Additional Considerations | Rope Type | Consider the specific application and choose a rope type that is suitable for the task. For example, kernmantle ropes offer excellent strength and durability, while static ropes are ideal for positioning and work positioning. |
| Rope Diameter | A larger diameter rope generally offers greater strength and durability, but it may also be heavier and less flexible. | |
| Inspection and Maintenance | Implement a rigorous inspection and maintenance program to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. |

How Should Safety Ropes Be Stored?
The way you store your safety ropes can significantly impact their lifespan and performance. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your ropes remain in optimal condition and ready for use:
Storage Environment
- Cool and Dry: Store ropes in a cool, dry location, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Exposure to heat, humidity, or freezing conditions can degrade the rope’s material and reduce its strength.
- Avoid Heat Sources: Keep ropes away from heat sources such as radiators, heaters, or open flames. Excessive heat can accelerate aging and weaken the fibers.
- Chemical-Free Zone: Store ropes in a place where they won’t be exposed to chemicals, solvents, or other corrosive substances. Chemical exposure can damage the rope’s outer sheath and compromise its internal structure.
Proper Coiling
- Loose Coiling: Coil the rope loosely to prevent kinking. Kinks can weaken the rope and create stress points that may lead to failure.
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Avoid sharp bends or tight coils, as these can damage the rope’s fibers.
- Inspect for Damage: Before storing the rope, inspect it for any signs of wear, tear, or damage. If any issues are found, the rope should be retired and replaced.

What Training is Required to Use Safety Ropes?
It is like other suspended platform parts, to ensure the safety of workers utilizing safety ropes, comprehensive training is imperative. This training should encompass the following key areas:
1. Rope Selection
- Understanding Rope Types: Workers should be familiar with different types of safety ropes, including static, dynamic, and work positioning ropes.
- Matching Rope to Task: Training should equip workers to select the appropriate rope for specific tasks, considering factors such as weight capacity, fall distance, and environmental conditions.
2. Rope Tying Techniques
Tying construction safety rope knots correctly is an important step.
- Essential Knots: Workers should be proficient in tying various knots, such as the figure-eight knot, the clove hitch, and the prusik knot.
- Proper Knot Placement: Training should emphasize the correct placement of knots to ensure optimal safety and efficiency.
3. Inspection Procedures
- Pre-Use Inspection: Workers should be trained to conduct thorough pre-use inspections of their safety ropes, checking for signs of wear, damage, or deterioration.
- Regular Inspections: Training should cover the frequency and procedures for regular inspections, as outlined by the manufacturer’s guidelines.
4. Emergency Procedures
- Fall Arrest Techniques: Workers should be trained on proper fall arrest techniques, including self-rescue methods.
- Emergency Response Plans: Training should cover emergency response procedures, such as alerting emergency services and providing first aid to injured individuals.

Safeguard Your Workforce
Follow the guide provided by construction equipment expert CPTC now! Regular inspection, proper selection, appropriate storage, and comprehensive training are crucial elements in maintaining a safe work environment. Remember, a well-maintained safety rope is a reliable tool that can save lives. Prioritize safety, invest in quality equipment, and adhere to best practices to ensure the well-being of your workforce.
Related Products
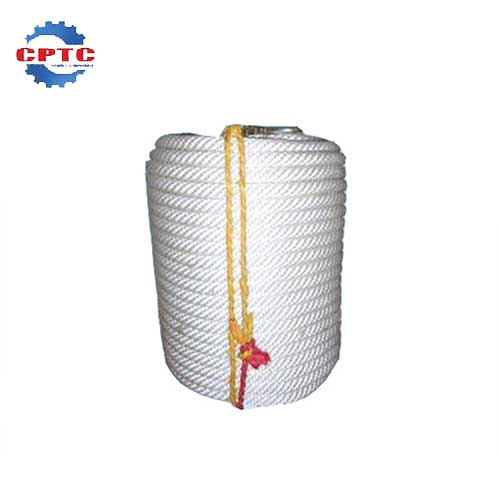
Safety Rope
Lightweight and Portable
Durable and Long-lasting
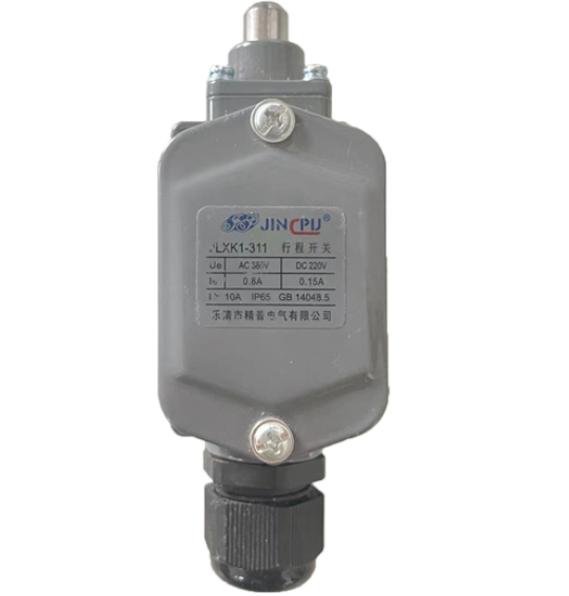
Limit Switch
Compact and Lightweight
Easy Installation
Electromagnetic Brake Coil
Electromagnetic Brake Coil
High-speed, high-precision control
Quick-acting, precise control
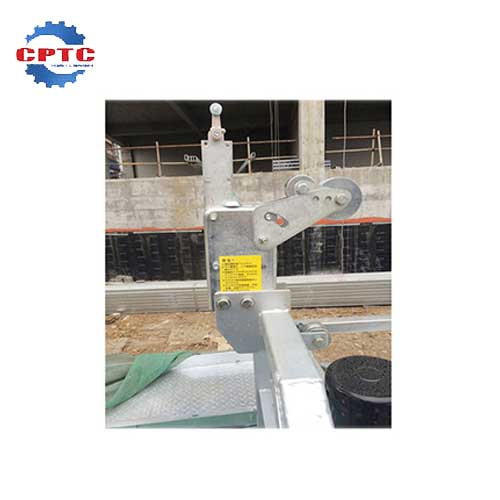
Suspended Platform Safety Lock
Easy to Operate and Use
Made…