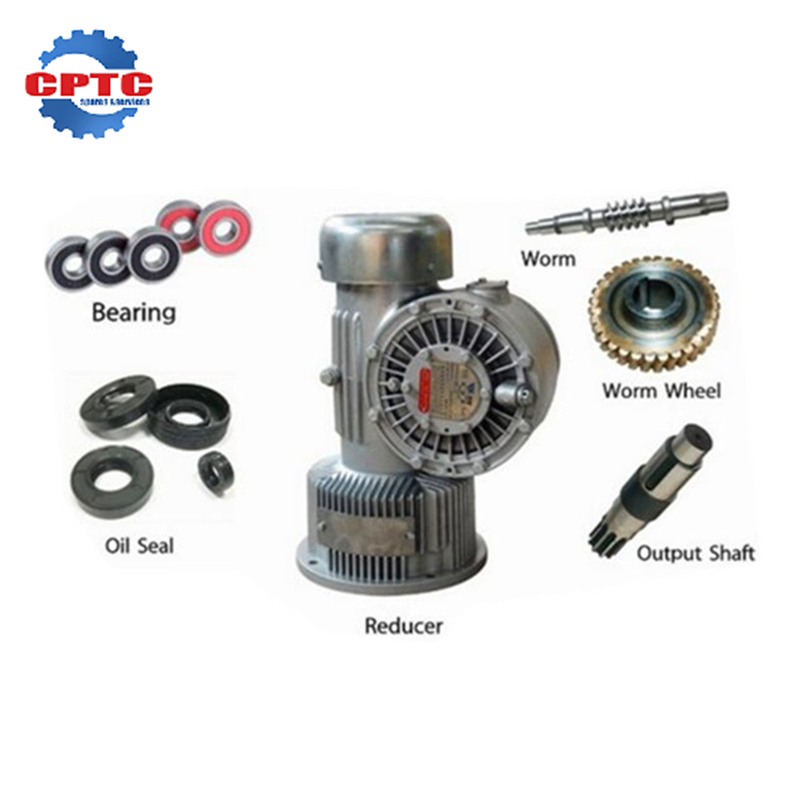
The intricate interplay between mechanical components within machinery often hinges on the effectiveness of power transmission systems. Among the various gear mechanisms employed, worm gears and worm shafts have carved a unique niche for themselves. These components, characterized by a helical thread on the worm meshing with teeth on the worm gear, offer distinct advantages that make them indispensable in a myriad of applications. From industrial machinery to automotive transmissions, the ubiquity of worm gear drives underscores their importance in modern engineering. This paper aims to elucidate the fundamental reasons why worm gears and worm shafts are so critical in transmission gearboxes and reducers.
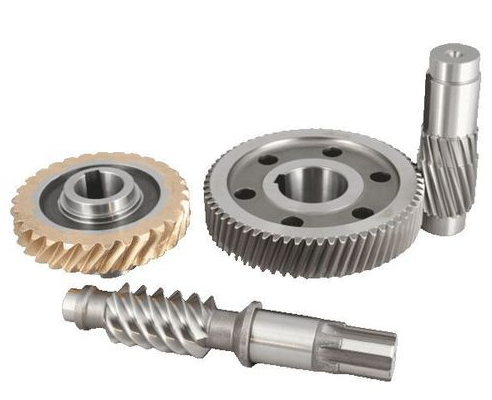

1. Working Principle of Worm Gears and Worm Shafts
Worm gear drives operate on a simple yet effective principle. A helical thread, known as the worm, engages with the teeth of a worm gear, which is perpendicular to the worm shaft. As the worm rotates, it forces the worm gear to turn at a slower rate due to the helical nature of the thread. This significant reduction in output speed results in a corresponding increase in torque, making worm gear drives ideal for applications requiring high torque and low speed.
2. Applications of Worm Gears and Worm Shafts in Transmission Gearboxes
Worm gears and worm shafts find extensive use in various types of transmission gearboxes due to their unique characteristics. These components play a crucial role in power transmission, speed reduction, and torque amplification.
2.1 Applications in Different Transmission Gearboxes
- Automotive transmissions: Worm gears are used for reverse gear mechanisms, transfer case differentials, and power steering systems. Their self-locking property is particularly advantageous for holding a vehicle in place on a hill.
- Industrial machinery: Worm gear reducers are widely used in heavy-duty applications such as conveyors, cranes, and mixers. They provide high torque output and compact design.
- Agricultural equipment: Worm gear drives are employed in tractors, combines, and other agricultural machinery for various functions, including ground speed control and power takeoff.
2.2 Implementing Gear Shifting with Worm Gears
- Sliding gear: A sliding gear mechanism can be incorporated into the worm gear drive to engage different gear ratios.
- Clutch-based shifting: A clutch can be used to disengage the worm gear from the driven shaft, allowing for gear changes.
- Synchronizers: Synchronizers can be employed to match the speeds of the input and output shafts before engaging a new gear, ensuring smooth gear shifting.
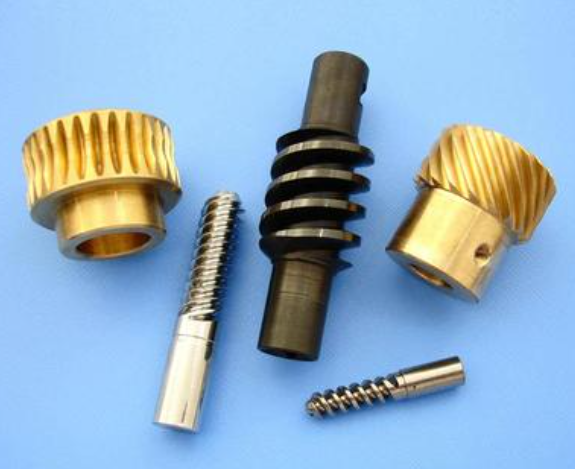

3. Applications of Worm Gears and Worm Shafts in Reducers
Worm gear drives are extensively employed in a wide range of reducers due to their unique characteristics. Their ability to provide high torque output, compact design, and smooth operation make them ideal for numerous industrial applications.
3.1 Application Scenarios in Various Reducers
- Heavy-duty machinery: Cranes, hoists, and conveyors often utilize worm gear reducers to provide the necessary torque and speed reduction for lifting and moving heavy loads.
- Material handling equipment: Forklifts, stackers, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) employ worm gear reducers for steering, lifting, and driving mechanisms.
- Packaging machinery: Worm gear reducers are used in packaging lines for conveying products, controlling speeds, and providing precise positioning.
- Machine tools: Lathes, milling machines, and drilling machines often incorporate worm gear reducers to drive feed mechanisms and spindle speeds.
3.2 Transmission Ratio Range and Load Capacity
Worm gear reducers offer a wide range of transmission ratios, allowing for significant speed reductions. The specific ratio can be tailored to meet the requirements of different applications. Additionally, worm gear reducers can handle substantial loads due to the large contact area between the worm and worm gear. The load capacity is influenced by factors such as the material properties, gear geometry, and lubrication.
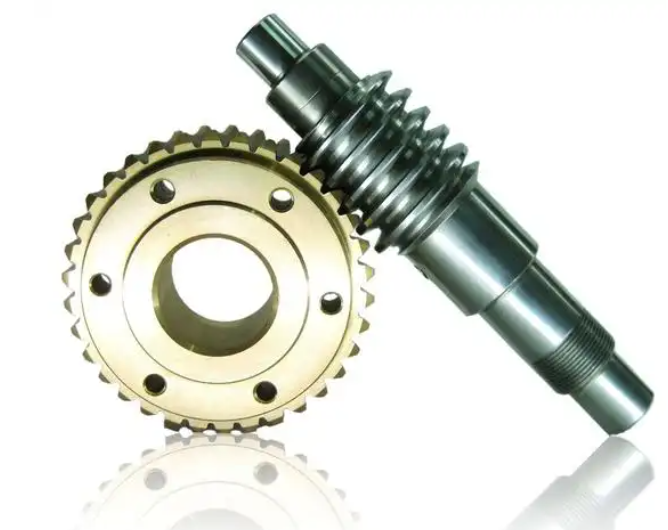

4. The Significance of Worm Gear and Worm Shaft Applications
- Efficiency: While worm gear drives generally have lower efficiency compared to other gear types due to sliding friction, advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have significantly improved their efficiency. Moreover, in many applications, the high torque output and compact design outweigh the slight efficiency loss.
- Load Capacity: Worm gear drives can handle substantial loads due to the large contact area between the worm and worm gear. This makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications such as material handling equipment and industrial machinery.
- Self-Locking: The self-locking property is a critical advantage of worm gear drives, especially in applications where it is necessary to hold a load in position without additional braking mechanisms. This feature is commonly used in automotive transmissions, elevators, and conveyors.
In conclusion, worm gears and worm shafts have proven to be invaluable components in transmission gearboxes and reducers. Their unique characteristics, including high torque capacity, compact design, and self-locking properties, make them indispensable in a wide range of applications. If you want to get more information about them, you can contact CPTC now!
Related Products
Construction Hoist Gearbox and Parts
Trademark: CPTC, GJJ, PET, BAODA
Passenger…
ABB Inverter
Green and environmentally friendly;
Customized services.
Coupling
Wide range of applications
Gear structure, welded connection method
Easy…
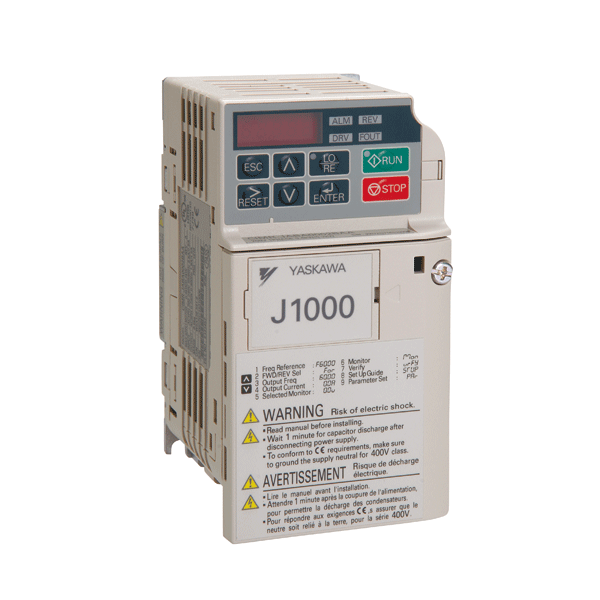
Yaskawa Inverter
Customizable Options;
Precise Speed Control;
Yaskawa inverter & Yaskawa inverter…